With the in-depth research in the fields of nanophotonics, surface plasmon polaritons, two-dimensional materials, and van der Waals heterostructures in recent years, scanning near-field optical microscopy(Scanning Near-field Optical Microscope, SNOM)It has become an indispensable representation tool for studying these fields. Although scanning near-field optical microscopy isScattering typepattern(s-SNOM)The spatial resolution has been greatly improved, but it still remains in practical useIt's very complicated.In this context, the United StatesMolecular VistaAs a result, a new generation was launchedScattering scanning near-field optical microscopeVista-SNOM!

Unlike traditional scanning near-field optical microscopes, Vista-SNOMBased on dedicatedLight induced force microscope(Photo-induced Force Microscope, PiFM)Technology, throughDetecting the relationship between the probe and the sampleDipole interaction directly obtains the field strength distribution on the sample surface without the need for far-field optical detectors. This not only eliminates interference from far-field signals, but also eliminates the need forSNOMConfigure multiple optical detectors with different frequency bands in that way. The detection end of the light induced force microscope can seamlessly adapt to UV~RF, and users only need to consider how to excite the excitation light to the sample.

The field strength results measured by Vista SNOM under light induced force microscopy mode are highly consistent with the simulation results, and it also has s-SNOM mode.This allows researchers to compare and analyze the PiFM field strength results with the s-SNOM field strength results.
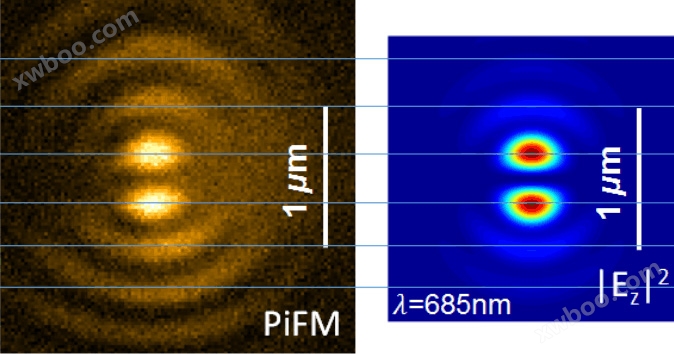
Case study of s-SNOM scattering scanning near-field optical microscope
The following figure shows the field strength distribution of gold aluminum dimer excited in different polarization directions at 480nm and 633nm. Do the measured field strengths in figures a and b match the theoretical simulations in figures c and d? The spacing between gold aluminum dimer is only5nm!

“Wavelength-dependent Optical Force Imaging of Bimetallic Al-Au Heterodimers,Nano Lett.2018”
The enhancement of Raman signals mentioned above is mainly due to the electromagnetic field enhancement of localized surface plasmon resonance (LSPR). The following figure shows the enhancement based on silver particle arraysSurface enhanced Raman spectroscopySubstrate(SERS)The field strength distribution in Figure f shows that the FWHM results of the light induced force microscope have been achieved3.1nmThe spatial resolution.

Fabrication and near-field visualization of a waferscale dense plasmonic nanostructured array,RSC Adv.2018”

